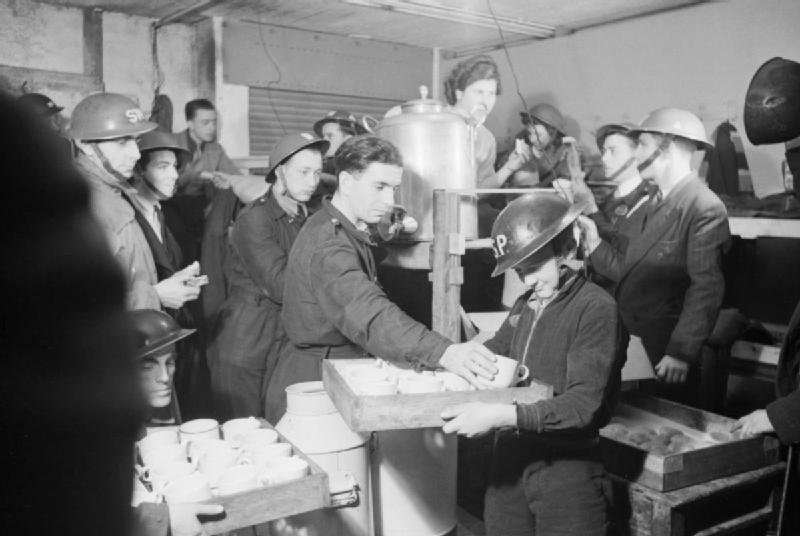
High Explosive Bomb at Holmewood Gardens
Description
High Explosive Bomb :
Source: Aggregate Night Time Bomb Census 7th October 1940 to 6 June 1941
Fell between Oct. 7, 1940 and June 6, 1941
Present-day address
Holmewood Gardens, Streatham Hill, London Borough of Lambeth, SW2 3TB, London
Further details
56 18 NW - comment:
Nearby Memories
Read people's stories relating to this area:
Contributed originally by kenyaines (BBC WW2 People's War)
After a few months of the tortuous daily Bus journey to Colfes Grammar School at Lewisham, I'd saved enough money to buy myself a new bicycle with the extra pocket money I got from Dad for helping in the shop.
Strictly speaking, it wasn't a new one, as these were unobtainable during the War, but the old boy in our local Cycle-Shop had some good second-hand frames, and he was still able to get Parts, so he made me up a nice Bike, Racing Handlebars, Three-Speed Gears, Dynamo Lighting and all.
I was very proud of my new Bike, and cycled to School every day once I'd got it, saving Mum the Bus-fare and never being late again.
I had a good friend called Sydney who I'd known since we were both small boys. He had a Bike too, and we would go out riding together in the evenings.
One Warm Sunday in the Early Summer, we went out for the day. Our idea was to cycle down the A20 and picnic at Wrotham Hill, A well known Kent beauty spot with views for miles over the Weald.
All went well until we reached the "Bull and Birchwood" Hotel at Farningham, where we found a rope stretched across the road, and a Policeman in attendance. He said that the other side of the rope was a restricted area and we couldn't go any further.
This was 1942, and we had no idea that road travel was restricted. Perhaps there was still a risk of Invasion. I do know that Dover and the other Coastal Towns were under bombardment from heavy Guns across the Channel throughout the War.
Anyway, we turned back and found a Transport Cafe open just outside Sidcup, which seemed to be a meeting place for cyclists.
We spent a pleasant hour there, then got on our bikes, stopping at the Woods on the way to pick some Bluebells to take home, just to prove we'd been to the Country.
In the Woods, we were surprised to meet two girls of our own age who lived near us, and who we knew slightly. They were out for a Cycle ride, and picking Bluebells too, so we all rode home together, showing off to one another, but we never saw the Girls again, I think we were all too young and shy to make any advances.
A while later, Sid suggested that we put our ages up and join the ARP. They wanted part-time Volunteers, he said.
This sounded exciting, but I was a bit apprehensive. I knew that I looked older than my years, but due to School rules, I'd only just started wearing long trousers, and feared that someone who knew my age might recognise me.
Sid told me that his cousin, the same age as us, was a Messenger, and they hadn't checked on his age, so I went along with it. As it turned out, they were glad to have us.
The ARP Post was in the Crypt of the local Church, where I,d gone every week before the war as a member of the Wolf-Cubs.
However, things were pretty quiet, and the ARP got boring after a while, there weren't many Alerts. We never did get our Uniforms, just a Tin-Hat, Service Gas-Mask, an Arm-band and a Badge.
We learnt how to use a Stirrup-Pump and to recognise anti-personnel bombs, that was about it.
In 1943, we heard that the National Fire Service was recruiting Youth Messengers.
This sounded much more exciting, as we thought we might get the chance to ride on a Fire-Engine, also the Uniform was a big attraction.
The NFS had recently been formed by combining the AFS with the Local and County Fire Brigades throughout the Country, making one National Force with a unified Chain of Command from Headquarters at Lambeth.
The nearest Fire-Station that we knew of was the old London Fire Brigade Station in Old Kent Road near "The Dun Cow" Pub, a well-known landmark.
With the ARP now behind us,we rode down there on our Bikes one evening to find out the gen.
The doors were all closed, but there was a large Bell-push on the Side-Door. I plucked up courage and pressed it.
The door was opened by a Firewoman, who seemed friendly enough. She told us that they had no Messengers there, but she'd ring up Divisional HQ to find out how we should go about getting details of the Service.
This Lady, who we got to know quite well when we were posted to the Station, was known as "Nobby", her surname being Clark.
She was one of the Watch-Room Staff who operated the big "Gamel" Set. This was connected to the Street Fire-Alarms, placed at strategic points all over the Station district or "Ground", as it was known. With the info from this or a call by telephone, they would "Ring the Bells down," and direct the Appliances to where they were needed when there was an alarm.
Nobby was also to figure in some dramatic events that took place on the night before the Official VE day in May 1945 when we held our own Victory Celebrations at the Fire-Station. But more of that at the end of my story.
She led us in to a corridor lined with white glazed tiles, and told us to wait, then went through a half-glass door into the Watch-Room on the right.
We saw her speak to another Firewoman with red Flashes on her shoulders, then go to the telephone.
In front of us was another half-glass door, which led into the main garage area of the Station. Through this, we could see two open Fire-Engines. One with ladders, and the other carrying a Fire-Escape with big Cart-wheels.
We knew that the Appliances had once been all red and polished brass, but they were now a matt greenish colour, even the big brass fire-bells, had been painted over.
As we peered through the glass, I spied a shiny steel pole with a red rubber mat on the floor round it over in the corner. The Firemen slid down this from the Rooms above to answer a call. I hardly dared hope that I'd be able to slide down it one day.
Soon Nobby was back. She told us that the Section-Leader who was organising the Youth Messenger Service for the Division was Mr Sims, who was stationed at Dulwich, and we'd have to get in touch with him.
She said he was at Peckham Fire Station, that evening, and we could go and see him there if we wished.
Peckham was only a couple of miles away, so we were away on our bikes, and got there in no time.
From what I remember of it, Peckham Fire Station was a more ornate building than Old Kent Road, and had a larger yard at the back.
Section-Leader Sims was a nice chap, he explained all about the NFS Messenger Service, and told us to report to him at Dulwich the following evening to fill in the forms and join if we still wanted to.
We couldn't wait of course, and although it was a long bike ride, were there bright and early next evening.
The signing-up over without any difficulty about our ages, Mr Sims showed us round the Station, and we spent the evening learning how the country was divided into Fire Areas and Divisions under the NFS, as well as looking over the Appliances.
To our delight, he told us that we'd be posted to Old Kent Road once they'd appointed someone to be I/C Messengers there. However, for the first couple of weeks, our evenings were spent at Dulwich, doing a bit of training, during which time we were kitted out with Uniforms.
To our disappointment, we didn't get the same suit as the Firemen with a double row of silver buttons on the Jacket.
The Messenger's Uniform consisted of a navy-blue Battledress with red Badges and Lanyard, topped by a stiff-peaked Cap with red piping and metal NFS Badge, the same as the Firemen's. We also got a Cape and Leggings for bad weather on our Bikes, and a proper Service Gas-Mask and Tin-Hat with NFS Badge transfer.
I was pleased with it. I could definitely pass for an older Lad now, and it was a cut above what the ARP got.
We were soon told that a Fireman had been appointed in charge of us at Old Kent Road, and we were posted there. After this, I didn't see much of Section-Leader Sims till the end of the War, when we were stood down.
Old Kent Road, or 82, it's former LFB Sstation number, as the old hands still called it,was the HQ Station of the District, or Sub-Division.
It's full designation was 38A3Z, 38 being the Fire Area, A the Division, 3 the Sub-Division, and Z the Station.
The letter Z denoted the Sub-Division HQ, the main Fire Station. It was always first on call, as Life-saving Appliances were kept there.
There were several Sub-Stations in Schools around the Sub-Division, each with it's own Identification Letter, housing Appliances and Staff which could be called upon when needed.
In Charge of us at Old Kent Road was an elderly part-time Fireman, Mr Harland, known as Charlie. He was a decent old Boy who'd spent many years in the Indian Army, and he would often use Indian words when he was talking.
The first thing he showed us was how to slide down the pole from upstairs without burning our fingers.
For the first few weeks, Sid and I were the only Messengers there, and it was a very exciting moment for me to slide down the pole and ride the Pump for the first time when the bells went down.
In his lectures, Charlie emphasised that the first duty of the Fire-Service was to save life, and not fighting fires as we thought.
Everything was geared to this purpose, and once the vehicle carrying life-saving equipment left the Station, another from the next Station in our Division with the gear, would act as back-up and answer the next call on our ground.
This arrangement went right up the chain of Command to Headquarters at Lambeth, where the most modern equipment was kept.
When learning about the chain of command, one thing that struck me as rather odd was the fact that the NFS chief at Lambeth was named Commander Firebrace. With a name like that, he must have been destined for the job. Anyway, Charlie kept a straight face when he told us about him.
We had the old pre-war "Dennis" Fire-Engines at our Station, comprising a Pump, with ladders and equipment, and a Pump-Escape, which carried a mobile Fire-Escape with a long extending ladder.
This could be manhandled into position on it's big Cartwheels.
Both Fire-Engines had open Cabs and big brass bells, which had been painted over.
The Crew rode on the outside of these machines, hanging on to the handrail with one hand as they put on their gear, while the Company Officer stood up in the open cab beside the Driver, lustily ringing the bell.
It was a never to be forgotten experience for me to slide down the pole and ride the Pump in answer to an alarm call, and it always gave me a thrill, but after a while, it became just routine and I took it in my stride, becoming just as fatalistic as the Firemen when our evening activities were interrupted by a false alarm.
It was my job to attend the Company Officer at an incident, and to act as his Messenger. There were no Walkie-Talkies or Mobile Phones in those days, and the public telephones were unreliable, because of Air-Raids, that's why they needed Messengers.
Young as I was, I really took to the Fire-Service, and got on so well, that after a few months, I was promoted to Leading-Messenger, which meant that I had a stripe and helped to train the other Lads.
It didn't make any difference financially though, as we were all unpaid Volunteers.
We were all part-timers, and Rostered to do so many hours a week, but in practice, we went in every night when the raids were on, and sometimes daytimes at weekends.
For the first few months there weren't many Air-Raids, and not many real emergencies.
Usually two or three calls a night, sometimes to a chimney fire or other small domestic incident, but mostly they were false alarms, where vandals broke the glass on the Street-Alarms, pulled the lever and ran. These were logged as "False Alarm Malicious", and were a thorn in the side of the Fire-Service, as every call had to be answered.
Our evenings were good fun sometimes, the Firemen had formed a small Jazz band.
They held a weekly Dance in the Hall at one of the Sub-Stations, which had been a School.
There was also a full-sized Billiard Table in there on which I learnt to play, with one disaster when I caught the table with my cue, and nearly ripped the cloth!
Unfortunately, that School, a nice modern building, was hit by a Doodle-Bug later in the War, and had to be demolished.
Charlie was a droll old chap. He was good at making up nicknames. There was one Messenger who never had any money, and spent his time sponging Cigarettes and free cups of tea off the unwary.
Charlie referred to him as "Washer". When I asked him why, the answer came: "Cos he's always on the Tap".
Another chap named Frankie Sycamore was "Wabash" to all and sundry, after a song in the Rita Hayworth Musical Film that was showing at the time. It contained the words:
"Neath the Sycamores the Candlelights are gleaming, On the banks of the Wabash far away".
Poor old Frankie, he was a bit of a Joker himself.
When he was expecting his Call-up Papers for the Army, he got a bit bomb-happy and made up this song, which he'd sing within earshot of Charlie to the tune of "When this Wicked War is Over":
Don't be angry with me Charlie,
Don't chuck me out the Station Door!
I don't want no more old blarney,
I just want Dorothy Lamour".
Before long, this song was taken up by all of us, and became the Messengers Anthem.
But this little interlude in our lives was just another calm before another storm. Regular air-raids were to start again as the darker evenings came with Autumn and the "Little Blitz" got under way.
To be continued.
Contributed originally by deirdre (BBC WW2 People's War)
Mark arrived in England with his grandmother in November 1942 to join his parents who were living in Balham. His father, Witold Krymer, was a good linguist, had taught himself English, and, after a stint at the Patriotic School in Victoria, was working for MI6 while Mark's mother was completing her degree in Polish Law at Oxford University (a special arrangement). Later she worked for the Polish government in exile in London.
Although they had all left Poland in September 1939, Mark had not seen his parents for two years and at six years old he did not remember them. He had also forgotten Polish, and only spoke French.
No stranger to war
Living in London was obviously very dangerous, and Mark recalls well the various bombing campaigns. His mother always refused to go to air raid shelters. One house, which they had lived in, was subsequently bombed, so she was lucky not to be there at that time.
Mark was no stranger to war - he remembered the German bombers coming over Warsaw on 1 September 1939, even though he was only three - it was to change his life.
Paris and Warsaw babyhood
Mark had been born in 1936 in Paris to Polish parents studying there and they returned home to Warsaw, where Mark remembered his swing attached to the door-frame in the flat where they lived (the flat survived in bombed out Warsaw).
Once it was clear that the Germans had overwhelmed the Polish forces with their bombing and tanks, Witold Krymer (with Protestant-Jewish parentage) was keen to leave before the Germans arrived in the city. He managed to get his family into Lithuania (agreeing to take a couple of generals' wives so he could obtain petrol for the car).
Journey to safety
The family embarked on a fraught trek through the Baltic states to reach France. The most immediate problem was money to pay for living expenses and border guides. The Russians controlled the Baltic states, and a Russian officer in a cafe took pity on the little boy, ordering some food. Maybe he was missing a son back home.
Witold Krymer managed to obtain some cash by trading watches - desperate measures born of a desperate situation - and with considerable difficulty and danger the family made it through to Estonia and caught the last boat out to Sweden. They had planned to go to the USA, but Mark fell ill and, thinking it was scarlet fever, his father decided to join family members already living in France in 1940. That could have been a dreadful mistake.
Alerted to the German invasion of France, the parents made a dash for England, leaving Mark behind in the care of his grandmother. Mark's father, having joined the Polish forces in England, was eventually able to get Mark and his grandmother to England, via Spain and Portugal when the Germans occupied the Vichy area and it became very dangerous for refugees to remain in France.
Now in England and back to school
A few months after Mark's arrival, his mother was about to give birth to another baby, and his father asked a policeman to stay and look after Mark in the family home while he took his wife to hospital.
Mark first attended a French-speaking school, and then a Catholic school, where he felt rather isolated as a Protestant. After attending another local school, Mark went to a boarding school in Devon, where he remembers seeing the excercises for the D-day landings on the north Devon coast. Like most little boys are the time, he took great interest in the more evident aspects of the war, knowing about the different types of bombs and planes.
Home from school, Mark recalled the excitement of VE Day in London. With the momentous changes in his Polish home, his future life was to be in England and he became a British citizen in 1948.
Contributed originally by Pamela_Newbery (BBC WW2 People's War)
As I was only 3 years old when WW2 began, I have no memories of before the war. In about 1943 I was given a banana by a soldier on
leave from Africa, but I had no idea what it was or what to do with it. On being shown how to peel it, I then took half an hour to eat it, savouring every mouthful.
I wonder if the other local children who were also given a banana have similar memories.
These days bananas are so plentiful that younger people will not realise what aluxury they were in the 1940's.
On the rare ocassions when the greengrocer had a delivery of oranges, my mother would collect up the childrens' green ration books, walk half a mile to the shop and then join the queue to bring back some oranges.I probably stayed like a dog in the kennel in our Morrison shelter.
Contributed originally by Peter R. Marchant (BBC WW2 People's War)
Don’t tell Adolf about the wonders of country living for a small city boy. Don’t tell Adolf about the exciting playgrounds of the bomb damaged houses. Don’t tell Adolf about the excitement of the search lights and the guns and don’t tell Adolf how he changed my early childhood into an adventure often frightening, but with vivid memories I recall to this day.
My very first ever memories are framed by the war. It must have been sometime in 1940 when I was almost four years old. Our family, my Mum and Dad and my older sister Thelma, were living in a Victorian row house in Clapham, London. This area has now become quite fashionable with house prices equal to my father’s life time income. Then, it was a working class neighborhood, clean and respectable, populated by postmen, mechanics and lorry driver tenants like my father. The only thing I can remember about the interior of the house was the Morrison shelter in the center of the bedroom. There I spent many weeks of isolation with a severe attack of the mumps in uncomprehending discomfort, picking at the grey paint of the cage unable to take anything more solid than my mother’s blancmange and barley water, her remedies for all known human ills. I’m sure my parents were grateful the authorities provided us with a combination bomb shelter, table and sick bed, although I wonder was anyone actually saved by this contraption? This was a time when one’s betters weren’t questioned; my family rarely doubted they must know what was best for us. For those who know only about more serious bomb protection the Morrison shelter consisted of a bed surrounded with stout wire mesh and a steel top on four corner legs about the right height for a table. The idea was to prevent the occupants from being crushed to death under falling masonry, a small sanctuary to wait in, listening for the scrape of shovels and praying to be rescued before the air ran out. In addition to the ugliness and awful paint its major flaw was the assumption that we would all be in bed when the house collapsed, a family so stunted by food rationing that we were able to sleep together comfortably in a double bed. Did Adolf realize the Morrison was part of the propaganda war designed to show the Germans that we English were just as viral as the master race; a people that only needed a tin bed as protection from their bombs?
As I got better I was allowed to play in the garden at the rear of the house. I remember it as long and narrow flanked on one side by the windows of a small factory making parachutes, or bully beef, or some other necessity for killing the enemy. The weather must have been hot as I recall the young women talking to me through open windows. They seemed happy in their factory routine and the pound or two a day they earned which was probably the best money they had ever made. Or were their smiles just for the rather shy little boy they gave the small pieces of chocolate and orange segments then as rare and sought after as black truffles? If there’s a page in the calendar that can marked as the beginning of my generally good relations with the opposite sex it’s probably spring 1940.
There are many more memories that come to me clearly but they are mixed in a jumble of time. It must have been after the serious bombing of London started in summer 1940 that my sister and I were evacuated. We were all caught up in a great sea of events and
if the choice for our parents was having us with them so we could all be reduced to rubble together or safe country life for their children, it was not difficult to decide which train to catch. An adult knows the terrors and uncertainty of the world and has worries beyond tomorrow but a small boy knows only the moment and thinks of an hour as an eternity if an ice cream is promised.
We were sent to live with a Mr. and Mrs. Daniels and their two sons on their small holding at Gidcott Cross, a junction of narrow country roads about six miles from the market town of Holsworthy in the county of Devon. The surrounding country was divided into small irregular fields on a plan lost in antiquity, surrounded by tall hedges topped with thick bushes and occasional trees.
Many evacuees have grim stories to tell and we were very lucky to be in the care of a loving couple who treated us like their own. The Daniels had a few acres near the house and some additional pasture rented nearby. On this they kept a few milk cows, all with pet names, Daisy, Sadie and Jessie, a pig or two and a muddy barnyard full of chickens. A pair of ducks stayed most of the year in a narrow rivulet that ran around the house. A female dog Sally, always ready for a rabbit hunt, followed us around everywhere when she was not ensuring a new supply of terriers. The farm house had, or rather has, as it seems little changed over the years, thick rough walls yearly whitewashed, four or five rooms in two stories under a thick thatched roof. The Daniel’s house was at the foot of gently sloping fields set back from the road with a pig barn on the left and the milking shed and hay storage on the right of the heavy slab stone front path.
Mr. Daniels was a member of the local Home Guard, a group of tough wiry men too old for immediate military service. There were no blunderbusses or pikes, but modern weapons were in short supply. Mr. Daniels had upgraded to a worn double barreled shot gun a deadly weapon in his hands as all the rabbits knew. At lane intersections old farm wagons loaded with rocks were ready to be pushed into a road block. One clever ruse was redirecting the road signs, a confused German being thought better than a lost one. Any one advancing down the road to Holsworthy would find them selves in Stibbs Cross with only one pub, a much less desirable place to take over. The home guard met regularly near our cottage for drill and comradeship. It was so popular that the institution lived on well after the war as a social club. These men knew every blade of grass for miles around and would have caused any German paratroopers much annoyance if Adolf the military genius had ordered landings in this remote corner of England.
When they were not repelling German invaders the Home Guard kept an eye on the Italians in the area. Up the road was the Big Farm, big because it had a barn large enough to house a half dozen trustee Italian prisoners of war working the land. Riding on farm wagons pulled by huge shire horses, as petrol was very scarce, they would stop outside our cottage on their way to the fields. They looked like old men to me though they were just young boys probably not yet 18, endlessly happy to be out of the war, captured by a humane enemy and ending up in this idyllic setting. They carved wooden whirligig toys with their pen knives for me and the nostalgic Italian songs they sang I can hear in my mind to this day.
It was a wonderland for we city kids with farm animals, the open country to explore and no shortages of food. The farm was in most ways self supporting, if you wanted a stew you shot a rabbit or two, or cut the throat of a chicken. I helped with the endless farm chores collecting eggs every day from the nest boxes, when the chickens were good enough to cooperate. Many chickens didn’t appreciate the conveniences we provided and made the job into an adventure searching the hedgerows for errant layers. No tinned or horrible dried food for us, everything was fresh as the vegetables pulled from the ground within sight of the front door. When we eventually returned to London my sister and I were noticeably well fed and quite fat, the battle for my waist line probably goes back that far!
Without modern conveniences it took most of the daylight hours to keep the house running and everybody was expected to pitch in. Another of my ‘helping’ jobs was to help fill the water barrel. With a small boy’s bucket and many trips I walked up the road a hundred feet, to the well hidden in a hedge tangled with wild roses, pushed the wooden cover aside and, after tapping on the surface to send the water spiders skimming out of the way, dipped in my bucket. This taught country ways very quickly and water became a precious commodity to be recycled for many uses until it was finally used to scrub down the flag stone floor. The water was heated in a large black iron kettle hung on a chain over a log fire in the inglenook fireplace the only source of heat in the house. Cooking had changed little over hundreds of years and savory stews and soups were made over the burning logs in large iron cauldrons. There was no electricity or gas in our cottage and finer cooking required Mrs. Daniels skillful fussing with a flimsy paraffin oven in the back room from where emerged a stream of delicious pasties, or covered pies, filled with a range of edibles that would have surprised even a Chinese cook. These pasties were brought out every meal covering the table with a smorgasbord of dishes from ham and egg, potato and wild berries, until finished. The men took them into the fields stuffed in their Home Guard haversacks and with a jug of local cider and after grueling days in the sun bringing in the harvest ate dinner sprawled against the hay stacks. The days ran with the cycle of the sun; the evenings were lit sporadically with a noisy pressured paraffin lantern and bedtimes were shadowy with the light of candles.
I remember my evacuation with the Daniels as an idyllic time although now I detect there must have been a feeling of abandonment and bewilderment long buried. One of my parent’s visits I didn’t recognize the lady with my father as my mother had just started wearing glasses. Later on, another visit, I wandered the lanes all day looking for them on a country walk they had taken and was tearfully relieved to find them sitting in a field eating sandwiches having no idea how upset I was at being left. Evacuation must have had a profound effect on many young children like me. My wife thinks that this experience is the cause of many of my strange ways and quirks of personality although I claim genius has its own rules.
My sister and I were returned to London after a couple of years in the country, the precise timing is vague in my memory. The aircraft bombing was much less now although the sirens still wailed for the occasional raid setting the guns booming on our local Clapham Common. I wish I still had my treasured collection of shrapnel from the antiaircraft shell bursts that rained down razor sharp fragments of torn steel and made being outside as dangerous as the bombing. These would be poignant reminders of this time so distant it feels like another life. Memories of my best friend Basil who always managed to find the pieces with serial numbers, the most coveted in our collection.
I recall one night the warning sirens sounded and the sky was lit by searchlight beams probing for the attackers. Within minutes the street was as bright as the sky, plastered with small oil filled fire bombs. They were everywhere causing small fires in the gardens and on the roofs of our street. One slid through the slates and wedged itself under the cooker of our upstairs neighbour, Mrs. Tapsfield. My father spent the night running up and down the stairs carrying buckets of dirt from the garden and spraying the cooked cooker with a stirrup pump. I can, even now 60 years later, see my mother next morning standing on a chair with a hat pin puncturing the hanging bladders of water filled ceiling paper from the flood upstairs. The fire bombs caused a lot of minor damage but they were all damped down and none of our neighbours lost more than a room or two. For many years after the sheet metal bomb fins would turn up when a new flower bed was dug deep. The trusty stirrup pump gathered dust in the coal cellar ready in case it was of need in another war in the new atomic age.
England was a very grey place with some rationing into the 50’s. For us kids Clapham was a wonderland of bomb damaged play houses and vacant rubble strewn lots. There were complete sides of buildings missing leaving the floors with wallpapered rooms precariously suspended. Bath tubs and staircases were stuck teetering to a wall with no apparent support stories up and the cellars were half filled with debris with only dusty tunnels for access. You can imagine the games these inspired for us boys. A special game was attacking and defending the half flooded abandoned concrete gun emplacements on Clapham Common and exploring the communal air raid shelters dug in the square. If only our parents had known!
How do you remember the events of a war time childhood? Memories are like a damaged film, occasional clear scenes separated by long stretches scratched and out of focus.
Through the often repeated stories distorted by their retelling; by today’s chance incidents that start a flow of thoughts to a half forgotten scene. Was it a page in a book or an E mail from a friend, who can tell the truth from imagination? I cannot be sure of the exact timing and the precise details of my experiences in WW2 they have been rounded off by time, and in this diary I have done my best. Although the accuracy may not be perfect and who can be sure in the valley of the shadow of memory, I hope to have conveyed the atmosphere of my experiences in these anecdotes.
Contributed originally by jogamble (BBC WW2 People's War)
My Grandfather was Flight Lieutenant Leonard Thomas Mersh and this is just a glimpse in his life during World War 2, like many of the pilots he has a number of log books, with many miles accounted for and the stories to go with them.
Len went to Woods Road School in Peckham and then on to Brixton School of Building, where he qualified as a joiner. In 1938 at 18 he joined the RAF Volunteer Reserve. At Aberystwyth he made the grade to be a pilot and was then sent to Canada for further training in Montreal and Nova Scotia Newfoundland where he gained his wings on Havards and Ansons.
Once back in England he went to Aston Downs and flew many aircraft across England, eventually he was posted to East Kirby in Norfolk attached to 57 Squadron Bomber Command. He flew many missions over Germany and France and as far as the Baltic. Missions included laying mines in the fjords where submarines and battleships where hidden. Dresden; Droitwich, Hamberg, Nuremberg, Brunswick and Gravenhorst were some of the places he bombed. Some times he carried the Grand Slam bomb.
In January 1945 he and his crew where sent to Stettin Harbour to lay mines at night. They where one of the lucky ones, as 350 planes had been sent and only 50 came back. Granddad’s plane was attacked by enemy fighters and was hit but they managed a second run over the target to release their mines.
In March 1945 during a sortie against Bohlen, his aircraft was attacked by a Junkers 88. The plane was hit but they made three bombing runs and then hedgehopped back to England.
On the 26th October 1945 Leonard was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross, (DFS), for courage, determination and efficiency.
After completing operational tours and six mine laying sorties he was drafted to 31 Squadron, Transport Command at the end of the Dutch Indonesian Campaign flying VIPs. He flew General Mansergh to Bali being the first RAF plane to land on March 8th 1945 to accept the Japanese surrender.
In 1948 Leonard was drafted to Germany to help with the Berlin Airlift. The squadron reopened airstrips which had been closed at the end of the war, plot routes into Berlin and get them working, the Americans would move in and the squadron would move on to another station. They flew by day and night and were lucky to gain 5hours sleep, which was taken in Mess chairs, which is perhaps why he caught TB, which ended his career and he then spent a lot of time in and out of hospital.